What's New
- A case study of Exemptia in Hidradenitis Suppurativa published in IJDVL Read More..
- A case of relapsing polychondritis with laryngeal stenosis successfully controlled with Exemptia’ accepted in Indian Journal of Rheumatology.



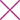
Uveitis is inflammation of Uvea which includes middle parts of eye such as iris, choroid and ciliary body. It can also affect other nearby parts of eye like retina, vitreous and optic nerve.
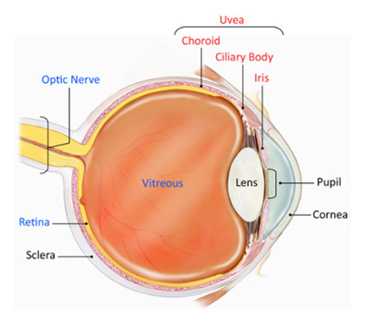
Uveitis caused by microorganisms such as bacteria and virus knows as Infectious Uveitis. Uveitis caused other than infection (Immune-mediated) is called non-infectious uveitis. Non-infectious uveitis is more common than infectious cases and main cause is defect in immune system.
There are several symptoms you may experience in one or both eyes which includes:
Non-infectious uveitis can be a chronic inflammatory condition.
A sudden appearance or worsening of symptoms is called a flare. Flares can recur over time.
If you have been experiencing any of these symptoms, or if you are having a recurrence, it’s a right time to talk to your doctor.
Exemptia helps in reduction of pain and redness in one or both eyes as well as reduces inflammation by blocking inflammation causing protein.
The recommended dose of Exemptia for adult patients with non-infectious Uveitis is an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg given every other week starting one week after the initial dose.
If you forget to take Exemptia, inject a dose as soon as you remember. Then, take your next dose at your regular scheduled time. This will put you back on schedule.
Exemptia is administered by subcutaneous injection so best sites are front of thighs or lower abdomen (belly). If you choose your abdomen do not use the area 2 inches around your belly button (navel).
Before injecting Exemptia, clean injection site with alcohol swab.
Hold the body of the prefilled syringe in one hand between the thumb and index finger. Hold the syringe in your hand like a pencil.
With our other hand gently squeeze the area of cleaned skin and hold it firmly.
Using a quick, dart- like motion, insert the needle into the squeezed skin at an angle of about 45degrees.
After the needle is in, let go of the skin. Pull back gently on the plunger.
Store Exemptia in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C in the original container until it is used. Protect from light.
When travelling, Exemptia should be stored in a cool carrier with an ice pack.
Do not freeze Exemptia. Do not use Exemptia if frozen, even if it has been thawed.
Refrigerated Exemptia may be used until the expiration date printed on the Exemptia carton and prefilled syringe.
Do not use the prefilled syringe if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or has flakes or particles in it.
Keep Exemptia, injection supplies and all other medicines out of the reach of children.
Understanding what triggers your psoriasis symptoms to flare can help you manage your disease.
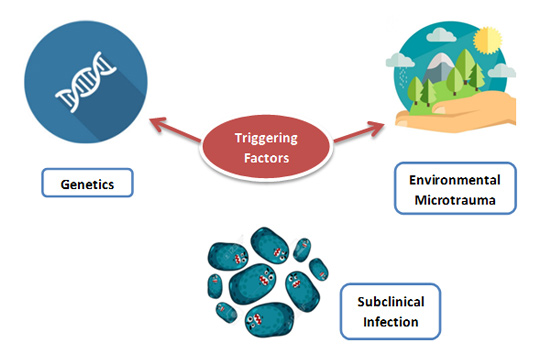
Stress is a trigger factor for uveitis. Having sufficient rest ensures that your body and eyes recover from daily exertions. Schedule some time to relax your eyes daily, even if only for 5 minutes.
You can meditate, go for a walk, do yoga in fresh air or simply do something you enjoy doing that will take your mind off your worries. This may to reduce the recurrence of your uveitis.
Smoking can worsens or triggers uveitis. The toxins contained within cigarette smoke (tobacco-specific nitrosamines) (ISNAs), benzene, pesticide, arsenic, cadmium, cyanide) will affect your health and how your body responds to illness. So if you do develop uveitis, it is possible that smoking may potentially delay your recovery from the inflammation.
Take plenty of fruits and vegetable while minimizing trans-fatty acids will benefit your overall eye health. Many fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants that are good for your eye health, such as spinach, peppers, cherries and blueberries.
Vitamins C and E are found to decrease the symptoms of anterior uveitis. The combination of vitamin C and vitamin E improved vision more.
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is also known for its antioxidant properties. It was found to help reduce the symptoms of chronic uveitis. Antioxidants may help to boost the immune system and may play a role in uveitis prevention.
Call us toll-free: 1800-123-2273
Visit: www.Exemptia.com
Exemptia is a medicine called a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker. Exemptia targets and blocks TNF-alpha. TNF plays a role in the process that causes inflammation. Because TNF blockers, including Exemptia, affect the immune system, they can lower the ability to fight infections and may cause side effects.
You take Exemptia by giving yourself an injection under the skin, every other week (one week after your initial starting dose). Exemptia cannot be taken by mouth. Do not try to inject Exemptia yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections. If your doctor decides that you are able to give your injections at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject Exemptia.
Please remember: Your first Exemptia injection should be given under the supervision of a nurse or health care professional. Always consult with your health care professional before you start taking Exemptia. You can call your doctor or 1800-123-CARE (1.800.123.2273) if you have questions about giving yourself an injection.
One of the most common side effects with Exemptia is injection site reactions such as pain, redness, rash, swelling, itching, or bruising. These symptoms usually will go away within a few days. If you have pain, redness, or swelling around the injection site that doesn’t go away within a few days or gets worse, call your doctor right away.
Signs of a serious allergic reaction include hives, trouble in breathing, and swelling of your face, eyes, lips, or mouth. Call your doctor right away if you experience any of these symptoms.
Your doctor will tell you how often to take an injection of Exemptia. Do not inject Exemptia more often than prescribed. If you need additional help with self-injecting, you can view an instructional video.
It may be a good idea to mark your calendar ahead of time with the dates of your Exemptia treatment. This may help you remember when to take it. Always follow your doctor's instructions on when and how often to take Exemptia.
If you forget to take Exemptia when you're supposed to, inject the next dose as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose when your next scheduled dose is due. This will put you back on schedule. If you're not sure when to inject Exemptia, call your doctor or pharmacist.
Your doctor will tell you how often to take an injection of Exemptia. Do not inject Exemptia more often than prescribed.
Yes, you can take certain other medicines if your doctor has prescribed them, or has told you it’s okay to take them while you're taking Exemptia. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take. You should not take Exemptia with abatacept, anakinra, infliximab, etanercept, certolizumab, or golimumab. Tell your doctor if you have ever used rituximab or azathioprine A rare type of cancer called hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, often resulting in death, has developed in some people. Most were male teenagers or young men with inflammatory bowel disease who were being treated with another medicine called azathioprine
Exemptia needs to be stored in a refrigerator 2°C-8°C in its original container and protected from light until it's used. Exemptia should never be put in the freezer or frozen. Do not use Exemptia if frozen, even if it has been thawed. Refrigerated Exemptia may be used until the expiration date printed on the prefilled syringe or Pen. Do not use a prefilled syringe if the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or has flakes or particles in it. Care should be taken to avoid dropping or crushing prefilled syringe as they contain glass.
If needed, for example when traveling, Exemptia may be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 25°C for a period of up to 14 days, with protection from light. Exemptia should be discarded if not used within the 14-day period.
When not traveling, your Exemptia prefilled syringe should be stored in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C in its original carton until you are ready to use it.
Once you remove your Exemptia Pen or prefilled syringe from the refrigerator, it must be used within 14 days. If not used within the 14 days, it must be discarded.
Once you’re Exemptia prefilled syringe has reached room temperature, it must be used within 14 days even if it is put back in the refrigerator. Exemptia that has reached room temperature must be discarded if it is not used within the 14-day period.
Do not use it and call your pharmacist immediately to let them know that your Exemptia prefilled syringe has been stored out of the refrigerator for more than 14 days. Your pharmacist will be able to advise you on how you may obtain a new Exemptia prefilled syringe.
Yes. Record the date when Exemptia is first removed from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton and dose tray.
If more comfortable, take your Exemptia prefilled syringe out of the refrigerator for 15-30 minutes before injecting to allow the liquid to reach room temperature. Do not remove the cap or cover while allowing it to reach room temperature. Do not warm Exemptia in any other way (for example, do not warm in a microwave or under hot water).
Always follow your doctor's instructions about when and how often to take Exemptia. Do not inject Exemptia more often than prescribed. If you need additional help with self-injecting, you can view an instructional video.
Unfortunately, there are no current medicines available that can cure your disease.
You should discuss the potential benefits and risks of Exemptia with your doctor. Exemptia is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker medicine that can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. You should not start taking Exemptia if you have any kind of infection unless your doctor says it is okay.
Serious infections have happened in people taking Exemptia. These serious infections include tuberculosis (TB) and infections caused by viruses, fungi, or bacteria that have spread throughout the body. Some people have died from these infections. Your doctor should test you for TB before starting Exemptia, and check you closely for signs and symptoms of TB during treatment with Exemptia. If your doctor feels you are at risk, you may be treated with medicine for TB.
Cancer: For children and adults taking TNF blockers, including Exemptia, the chance of getting lymphoma or other cancers may increase. There have been cases of unusual cancers in children, teenagers, and young adults using TNF blockers. Some people have developed a rare type of cancer called hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma. This type of cancer often results in death. If using TNF blockers including Exemptia, your chance of getting two types of skin cancer (basal cell and squamous cell) may increase. These types are generally not life-threatening if treated; tell your doctor if you have a bump or open sore that doesn’t heal.
Please see "What are the possible side effects with Exemptia?" for additional information regarding possible side effects. Also, please read the Medication Guide and discuss it with your doctor.
See more Important Safety Information for Exemptia.
Warning signs of a serious allergic reaction may include hives, swelling of your face, eyes, lips or mouth or trouble breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, call your doctor or seek emergency care immediately.
Studies have not been done to see how Exemptia interacts with food. If you have questions, talk to your doctor.
Studies have not been done to see how Exemptia interacts with alcohol. If you have questions, talk to your doctor.
As you may know, Exemptia affects the immune system and can lower your ability to fight infections like the seasonal flu. According to World Health Organization (WHO), the most effective way to prevent the flu is to get an annual vaccination.
Consult the doctor who prescribed your Exemptia before getting any vaccination.
You should not use Exemptia if you have an allergy to Exemptia or to any of the ingredients in Exemptia (including Succinic acid NF, sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride, L-Arginine Monohydrochloride, Sorbitol NF and polysorbate 80). The needle cover on the prefilled syringe contains natural rubber latex. Tell your doctor if you have any allergies to rubber or latex.
Tell your doctor about all of your health conditions, including if you:
Also tell your doctor about all the medicines you take. You should not take Exemptia with ORENCIA® (abatacept), KINERET® (anakinra), REMICADE® (infliximab), ENBREL® (etanercept), CIMZIA® (certolizumab pegol), or SIMPONI® (golimumab). Tell your doctor if you have ever used RITUXAN® (rituximab), IMURAN® azathioprine
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
If you are not sure or have any questions about any of this information, ask your doctor.
Exemptia can cause side effects, including:
Call your doctor or get medical care right away if you develop any of the above symptoms.
Common side effects of Exemptia include injection site reactions (pain, redness, rash, swelling, itching, or bruising), upper respiratory infections (sinus infections), headaches, rash, and nausea. These are not all of the possible side effects with Exemptia. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Remember, call your doctor right away if you have an infection or any signs of an infection, including:
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, breastfeeding, or plan to breastfeed. Exemptia should only be used during a pregnancy if needed. Women who are breastfeeding should talk to their doctor about whether or not to use Exemptia. Women and their doctor should decide whether to breastfeed or use Exemptia. You should not do both.