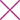
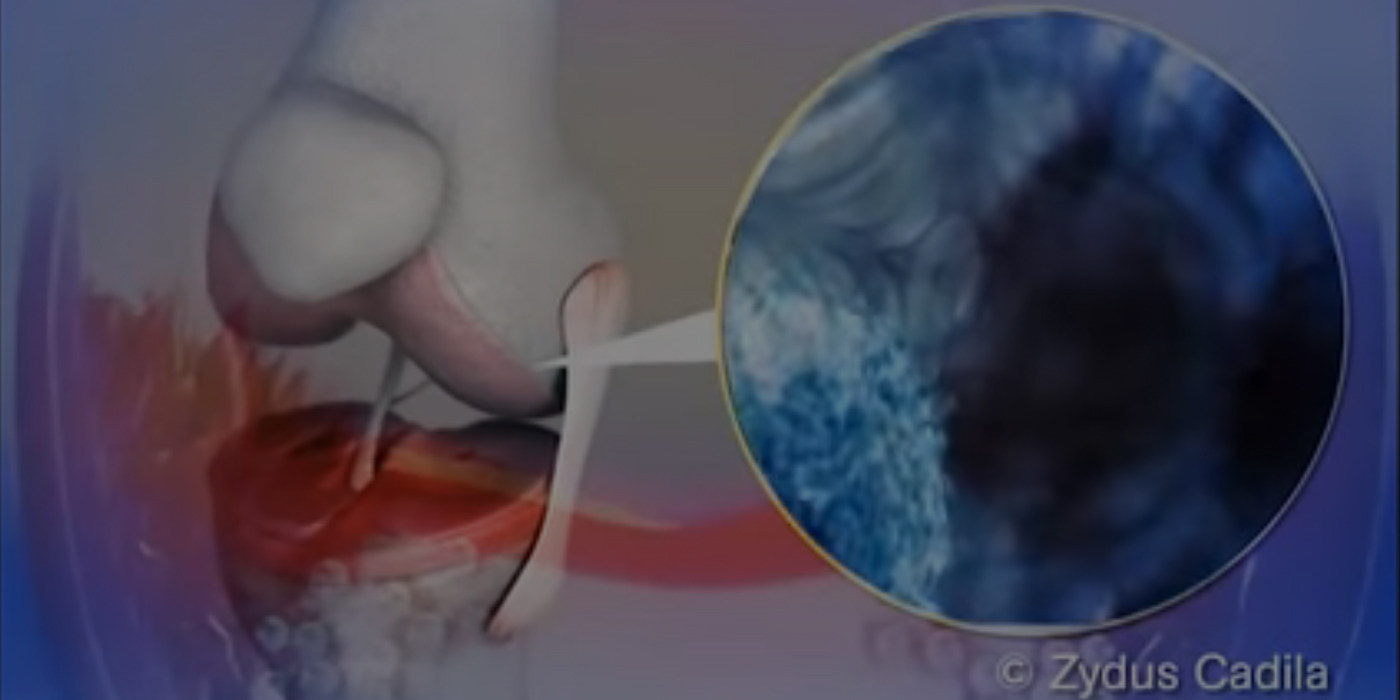
Overproduced TNF-α Leads to Inflammation of Synovial Membrane and Joint Damage in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS), Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) and Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA).
All Indication dosing details
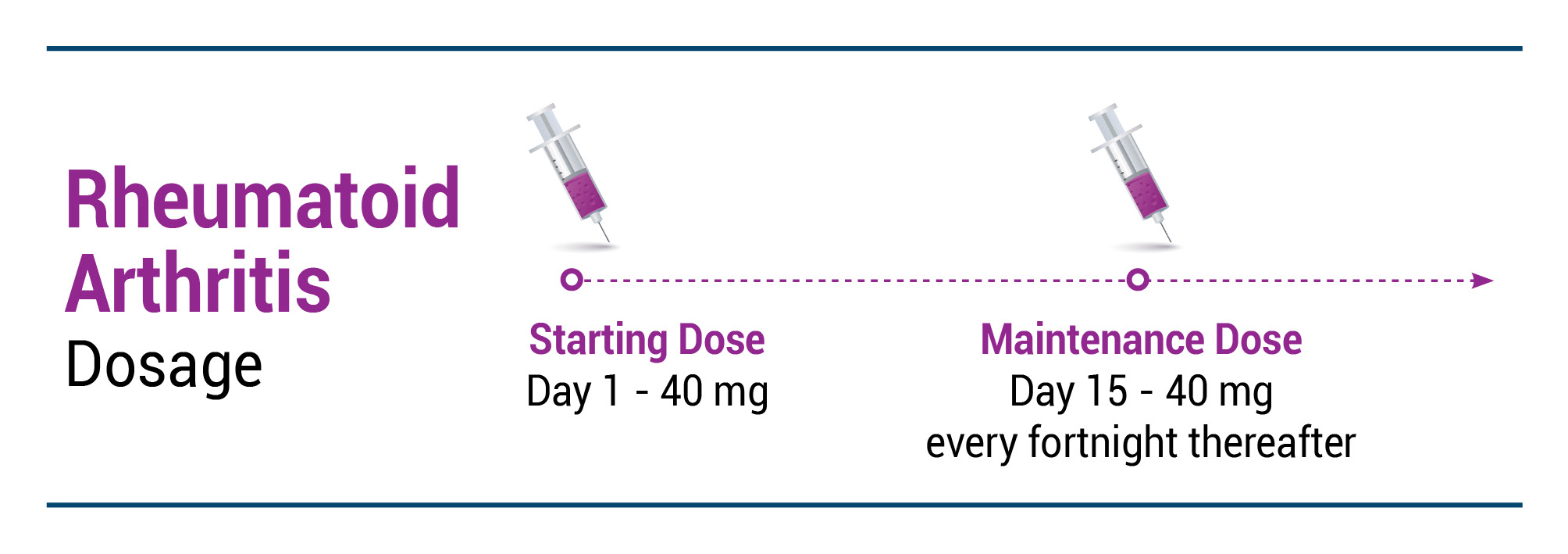
RA
EXEMPTIA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms such as improving clinical response, inhibiting the progression of joint damage and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis.
Recommended EXEMPTIA dose regimen:
AS
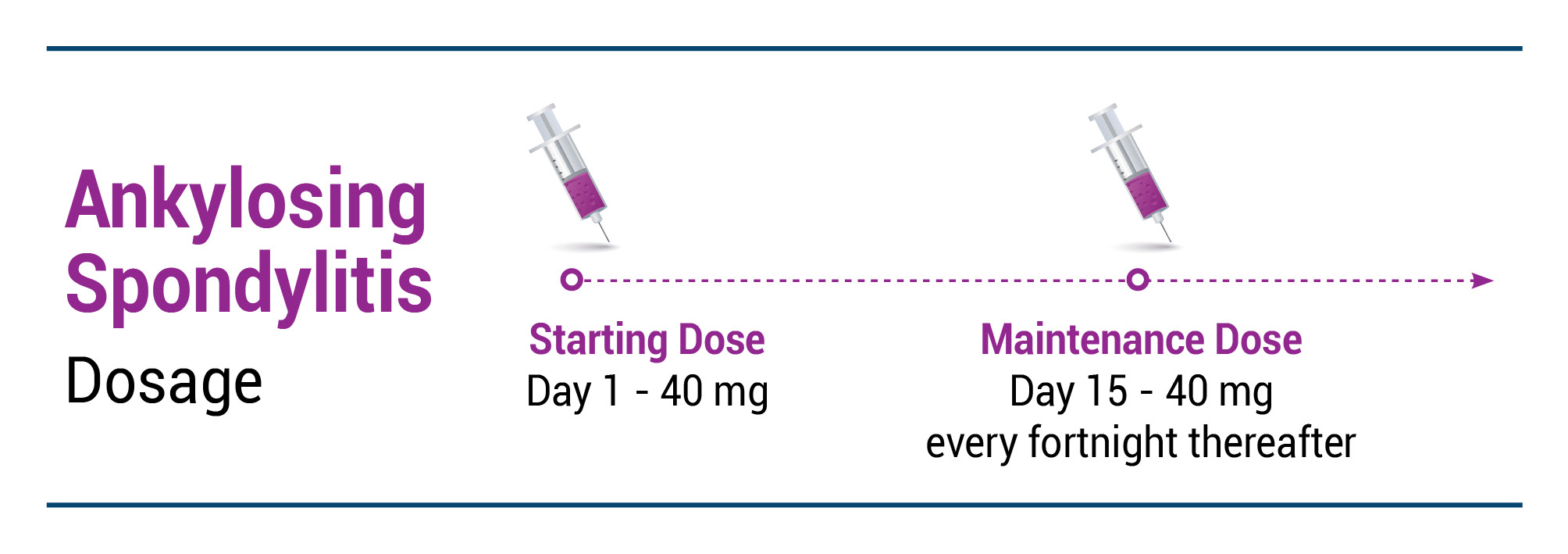
EXEMPTIA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis.
Recommended EXEMPTIA dose regimen:
PsA
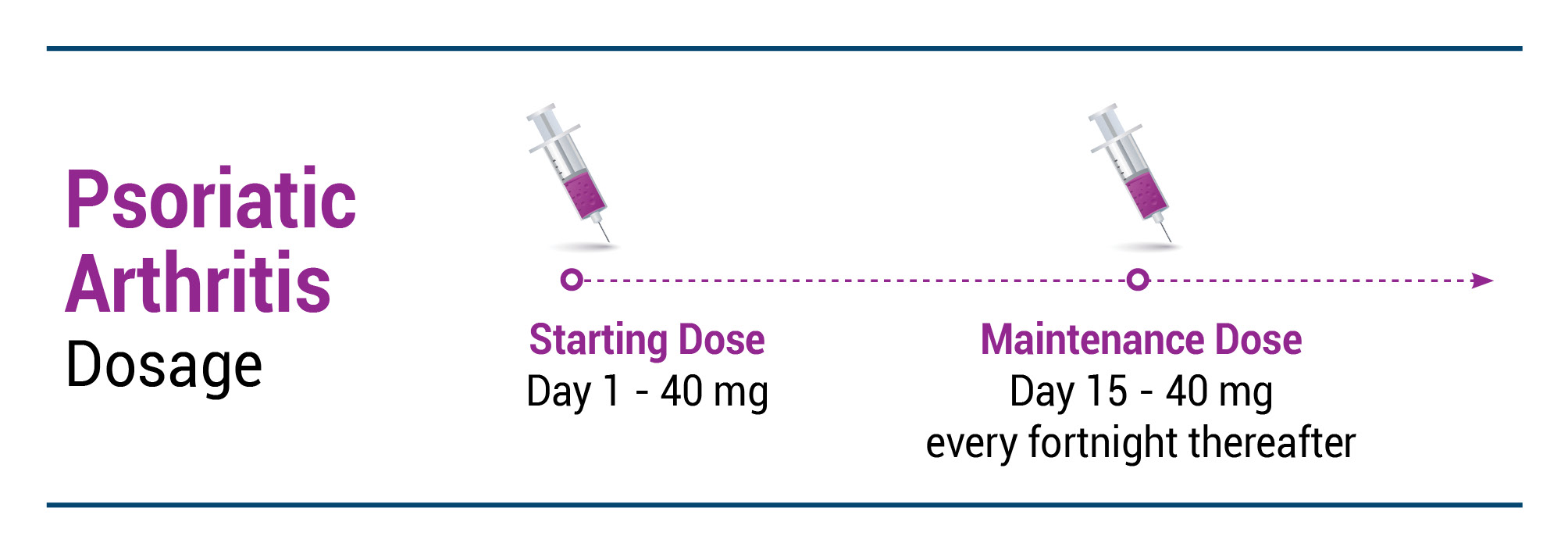
EXEMPTIA is indicated, alone or in combination with non-biologic DMARDs, for reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage and improving physical function in adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
Recommended EXEMPTIA dose regimen:
JIA
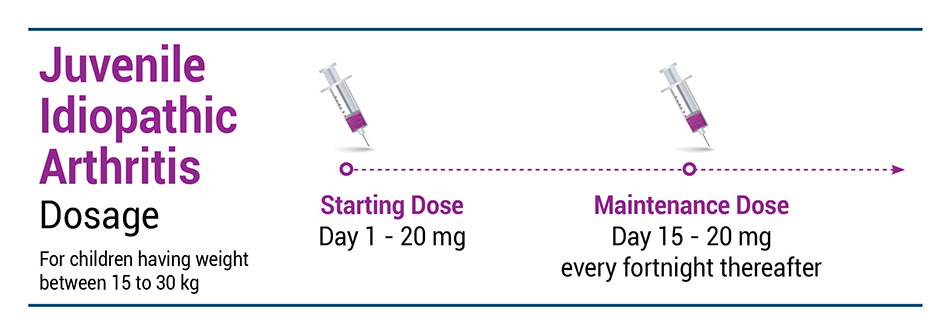
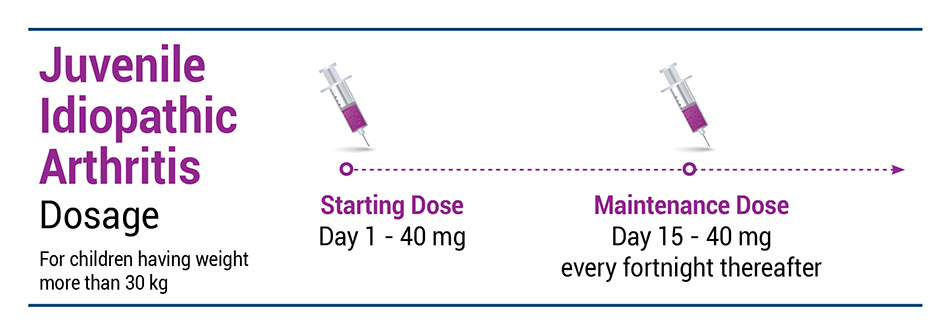
EXEMPTIA is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
Recommended EXEMPTIA dose regimen:
Real world Evidences of Exemptia
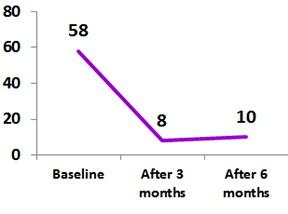
Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Clinical use of biosimilar Adalimumab (ZRC – 3197) in patients with inflammatory arthritis: A real life experience
A total 51 patients with Rheumatoid arthritis were participated in the study
All the patients had received biosimilar Adalimumab 40 mg every 15 days for initial 3 months.
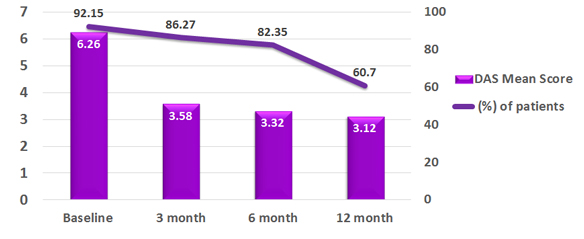
Clinical remission as defined by DAS28 < 2.6 was achieved in 11% of patients.
However, clinical response (defined as reduction in DAS28 > 1.2 from baseline) was achieved in 88% of these patients.1
Biosimilar Adalimumab was well-tolerated with no serious or unexpected side effects.
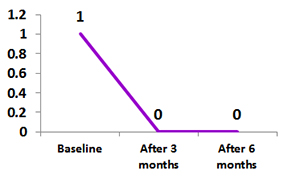
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Improvement in Disease activity and functional disability following treatment with biosimilar adalimumab in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
50 patients participated in the study and had received biosimilar Adalimumab 40 mg every 15 days for 24 week.
Following completion of bADA therapy, Significant reduction in disease activity and functional were observed.
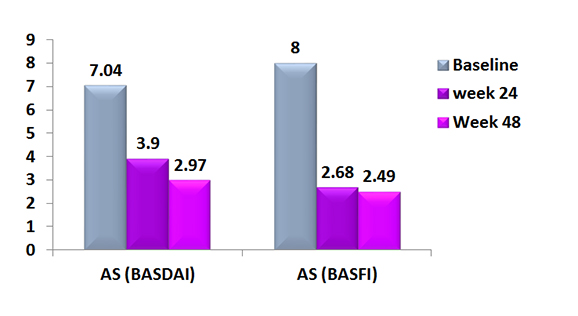
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis treated with Exemptia
Treatment was well tolerated and effectiveness maintained post therapy for up to one year.2
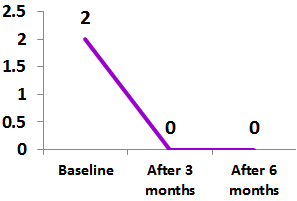
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Clinical use of ZRC 3197 (Adalimumab Biosimilar) in patients with Inflammatory Arthritis: A real life experience
A total 8 patients with Psoriatic arthritis were participated in the study.
All the patients had received biosimilar Adalimumab 40 mg every 15 days for 24 week.3
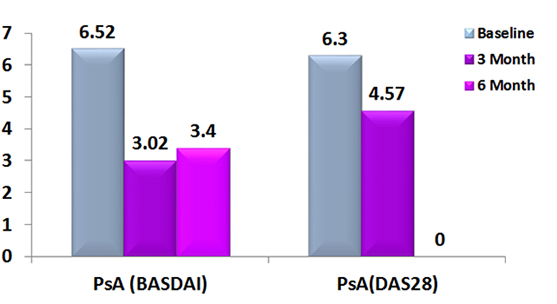
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and Disease Activity Score 28 Score in patients with Psoriatic Arthritis treated with Exemptia.
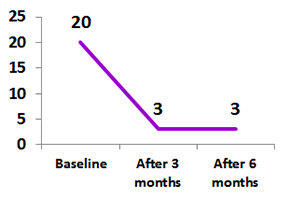
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
Use, Safety & Efficacy of ZRC 3197, a biosimilar candidate for reference Adalimumab from the Tertiary Pediatric Rheumatology Center in India
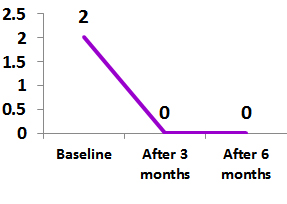
A total 15 patients with JIA participated in the study.
At 3 months 13 patients shows Exemptia was effective in primary and secondary endpints.
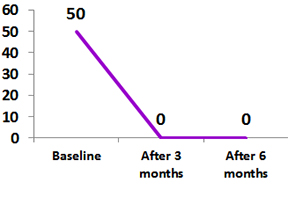
Median duration to achieve inactive disease in 12 children was 3 weeks 4
Ref:
- Clinical use of ZRC3197 (Adalimumab Biosimilar) in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis: A Real-life Experience. Journal of The Association of Physicians of India. 2017;65(5):22-25.
- Rao VK, Sudhakar A.Improvement in disease activity and functional disability following treatment with biosimilar adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis ; Proceeding of the ;APLAR/International Journal of Rheumatic Disease October/2017/20(1)
- Clinical use of ZRC3197 (Adalimumab Biosimilar) in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis: A Real-life Experience. Journal of The Association of Physicians of India. 2017;65(5):22-25.
- Agarwal M et al. Use, Safety and Efficacy of Zrc 3197, a Biosimilar Candidate for Reference Adalimumab (Humira) from a Tertiary Pediatric Rheumatology Centre in India: Proceeding of the ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting; September 28, 2016